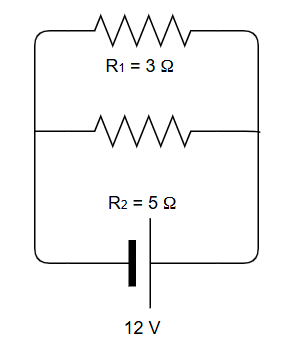
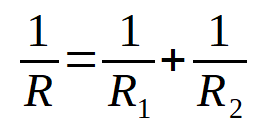Definition

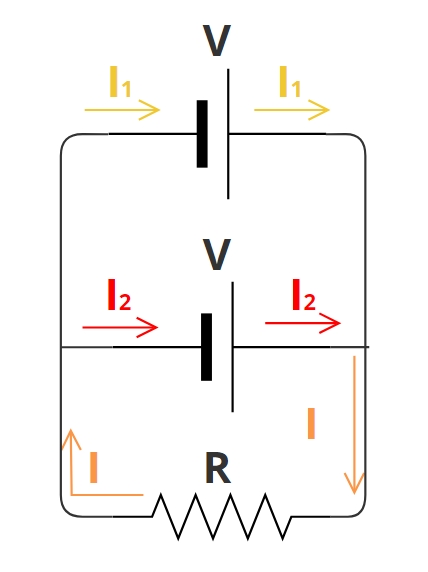
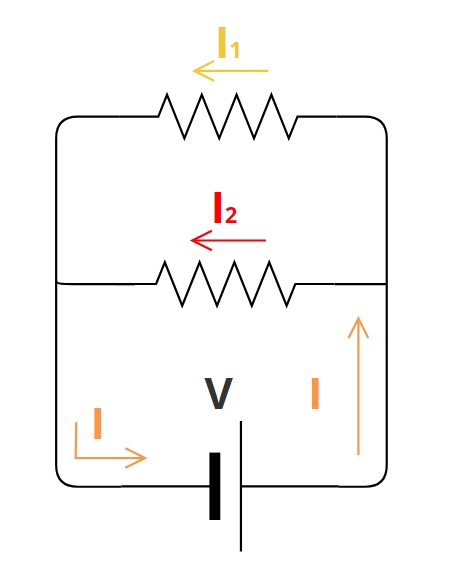
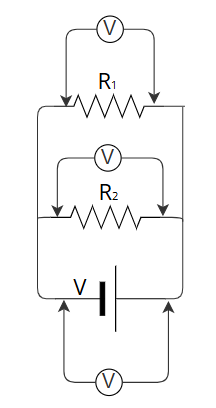
In a parallel circuit, the elements are conected so that the voltage is equal across each parallel component. If you look at how they are connected in the figure, you can see that, in this case, the wire is not a single continuous line with inserted elements, as it was in the series circuit. Now, the wire splits off into several lines, so that the electric current has more of one independent path to travel. These lines are usually represented in electrical diagrams as parallel to each other, hence its name.
The red arrows in the figure represent the current intensity.
PhET Interactive Simulations, University of Colorado Boulder, https://phet.colorado.edu , CC-BY-4.0