Ohm´s law
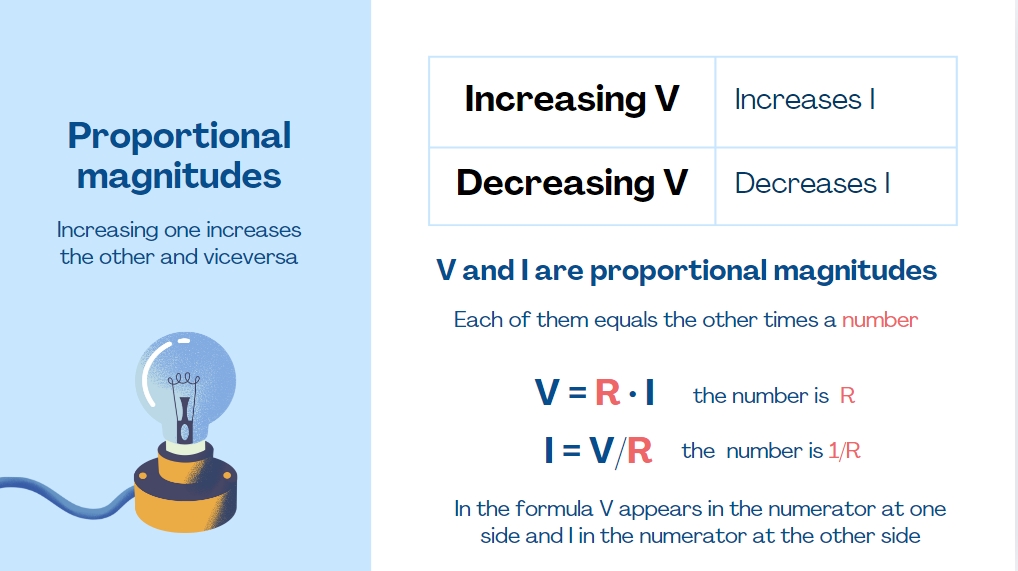
- Voltage (V), current (I) and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit are related to each other.
- As the resistance to the passage of charge increases, more energy is required to move the electrons. Therefore, voltage and resistance must be directly proportional.
- The greater the amount of charge we want to move per second (I), the greater the energy required, so voltage and current must also be directly proportional.

Ohm's Law describes this relationship:
V = I ⋅ times R
And it can also be expressed in these other ways, if what we want to calculate is I or R, instead of V:
I = V /dividedby R
R = V /divided by I
An easy way to memorize these equations, if you have trouble solving them, is with the triangle in the image. If you cover the magnitude you want to calculate with your hand, what you have left is the formula to calculate it.