Electric power
Power (P) is defined as the amount of energy (E) consumed per unit of time (t). In the international system it is measured in Watts (W).
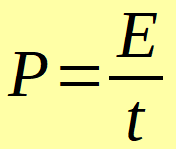
Energy can be related to voltage (V) as:
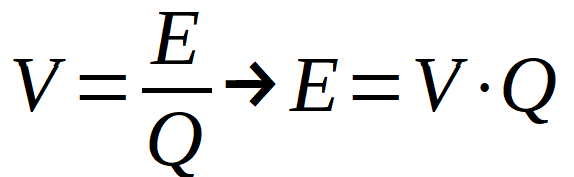
Q being the load. Dividing on both sides by time, and introducing the intensity value: I = Q /t :
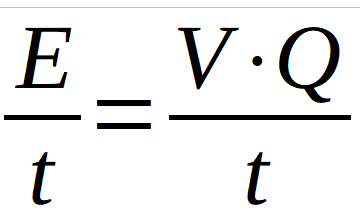
P = V · I
Understanding what power means will allow us to understand and control what we spend on electricity.
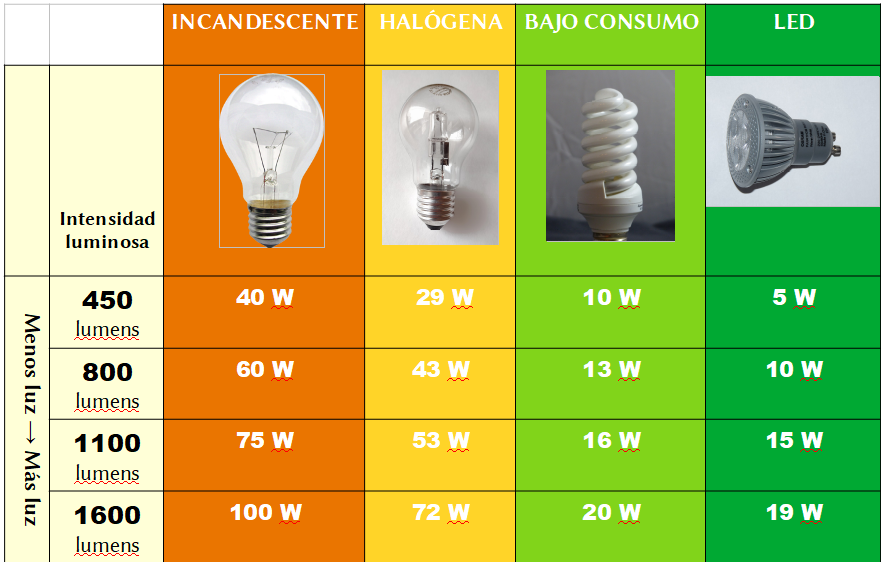
Look at the table. It shows 4 different types of light bulbs that can be used for lighting. Within each type, you can choose bulbs with a higher or lower luminous intensity (that give more or less light).
Let's say we need a light bulb for a room that requires a lot of light, for example the kitchen. If we buy an incandescent bulb, we need it to be 100 W to have the highest possible light intensity (1600 lumens), but if we choose an LED, a power of 19 W will be enough to give the same amount of light.
The 100 W bulb consumes 100 J of energy from the mains every second, while the 19 W bulb consumes 19 J in the same time.
Read on to see what difference it would make on your bill to use one bulb or another.
Audio: