Monera Kingdom
Monera kingdom
|
Monera kingdom is made up of bacteria, which are single-cell prokaryotic microrganisms. Most bacteria perform heterotrophic nutrition except Cyanobacteria, which can photosynthesize. Their size varies between 0.5 and 5 micrometres. They reproduce sexually through binary fission. Some bacteria may be alone or group together as Streptococcus (in chains) or Staphylococcus (in bunches). They may move agitating their flagella (a whip-like structure), or their *pili (some small hairs that are covering the surface of the bacteria). *(pilus: singular, pili: plural) |
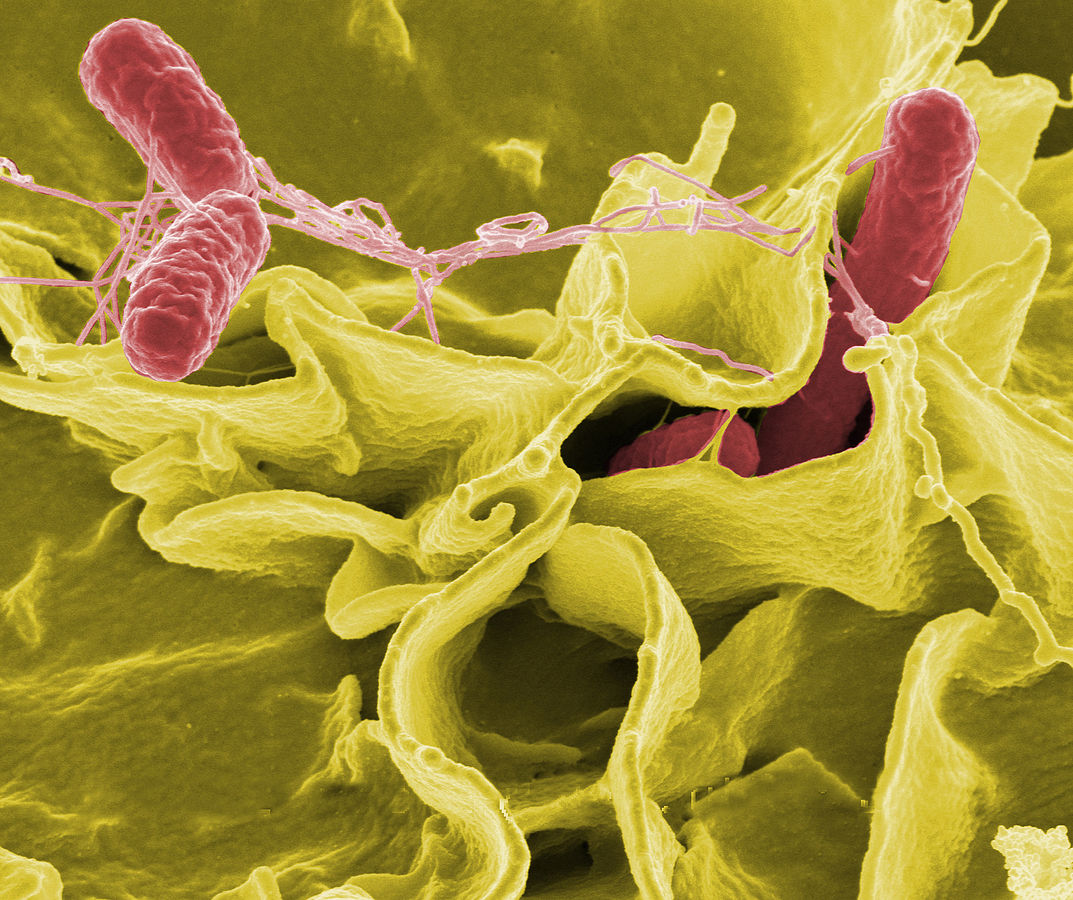
Colour-enhanced scanning electron micrograph showing Salmonella typhimurium (red) invading cultured human cells. National Institute of health. Wikipedia. (Public Domain)
|
||||||||||||

Spirilla. Wolframm Adlassnig. Wikipedia. (Public Domain)
|
There are a lot of bacteria in the human body especially on the skin and in the gut flora. They are harmless thanks to our immune system. But some bacteria are pathogenic and may cause diseases such as cholera, leprosy or tuberculosis. Bacteria are useful in the process of producing cheese and yogurt through fermentation. Others are used in mining to obtain gold or copper and some others help in the seawage treatment and the breakdown of oil spills. |
||||||||||||
|
|
Activity 1
Activity 2
Activity 3
Extra activity
Rosalind Franklin
Projects
|
Growing bacteria. Sick science. YouTube. (YouTube Standard Licence) |
PROJECT 1 Watch this video and try to grow bacteria taken from three different places. One of the members of the group can record all steps you take. At the end show the video to the classroom and explain all stages in your experiment. Write a report about the experiment too. |
|
PROJECT 2 Use this link to have a close look at a bacteria structure. Use plasticine, EVA foam, cardboard or any other material to elaborate a model of a bacteria. |
|
Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike License 4.0