Animal Kingdom
Animal Kingdom
Activity 3
Activity 4
Activity 5
Invertebrates
| INVERTEBRATES: There are six types of invertebrates: | ||
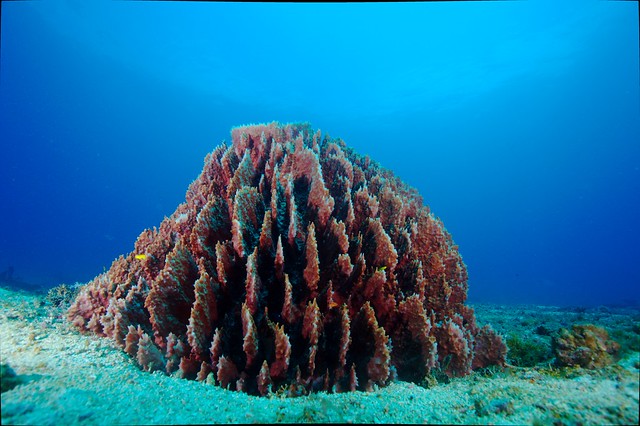

Sponge. Icelight. Flickr. (Pixabay licence)
|
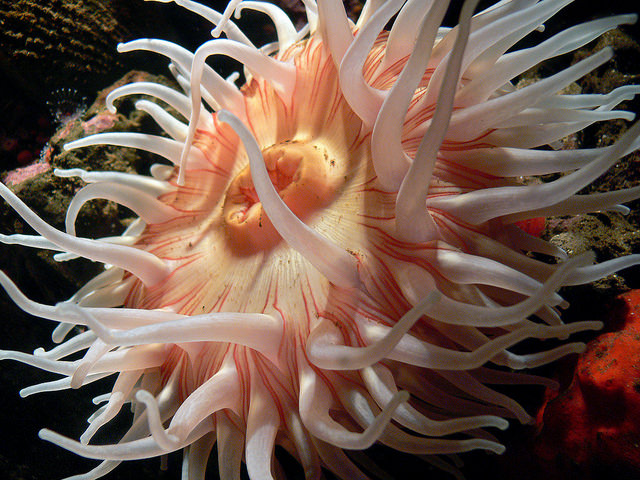

Anemone. Bernard Spragg. NZ . Flickr (Public Domain)
|

Caterpillar. FsHH. Pixabay. (Pixabay licence)
|
|
Sponges
Calcareous
Spicule
|
Cnidarians
Hydra
Anemone
|
Worms
Tube-shaped
Limbs
|
| MOLLUSCS: They are animals with a soft segmented body. Most of them have a calcareous shell. They live in aquatic habitats. Snails, mussels and octopusses are examples of molluscs. | ECHINODERMS: The are radially symmetrical animals with a calcareous endoskeleton and a water vascular system. Starfish, sea urchins and sea cucumber are examples of echinoderms. | ARTHROPODS: They are animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body and jointed appendages. The following are arthropods: insects (ants, dragonflies, beetles, etc.), arachnids (spiders, scorpions, ticks, etc.), crustaceans (crabs, lobsters, shrimps, etc.) and myriapods (centipedes, etc.) |
|
Molluscs
Shell
Mussels
|
Echinoderms
Endoskeleton
Sea urchin
|
Arthropods
Exoskeleton
Appendages
|
Actividade 6
Activity 7
Activity 8
Extra activity
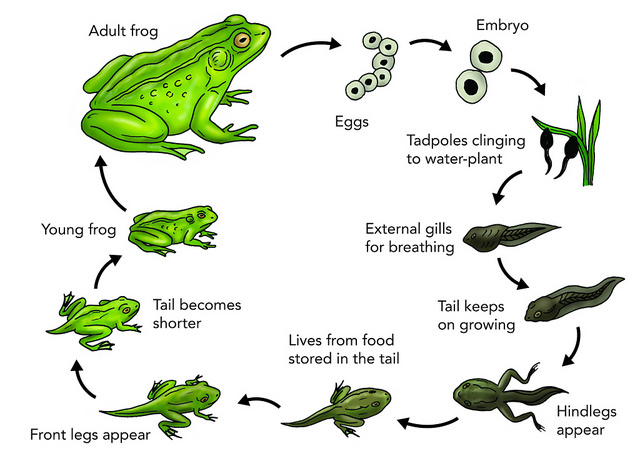
 1. Watch this photo about the frog life cycle. After observing the different phases, could you tell them aloud? 1. Watch this photo about the frog life cycle. After observing the different phases, could you tell them aloud? |
2. It is time to learn while playing. Here and here you have two games where you can practice what you have studied. | |
|
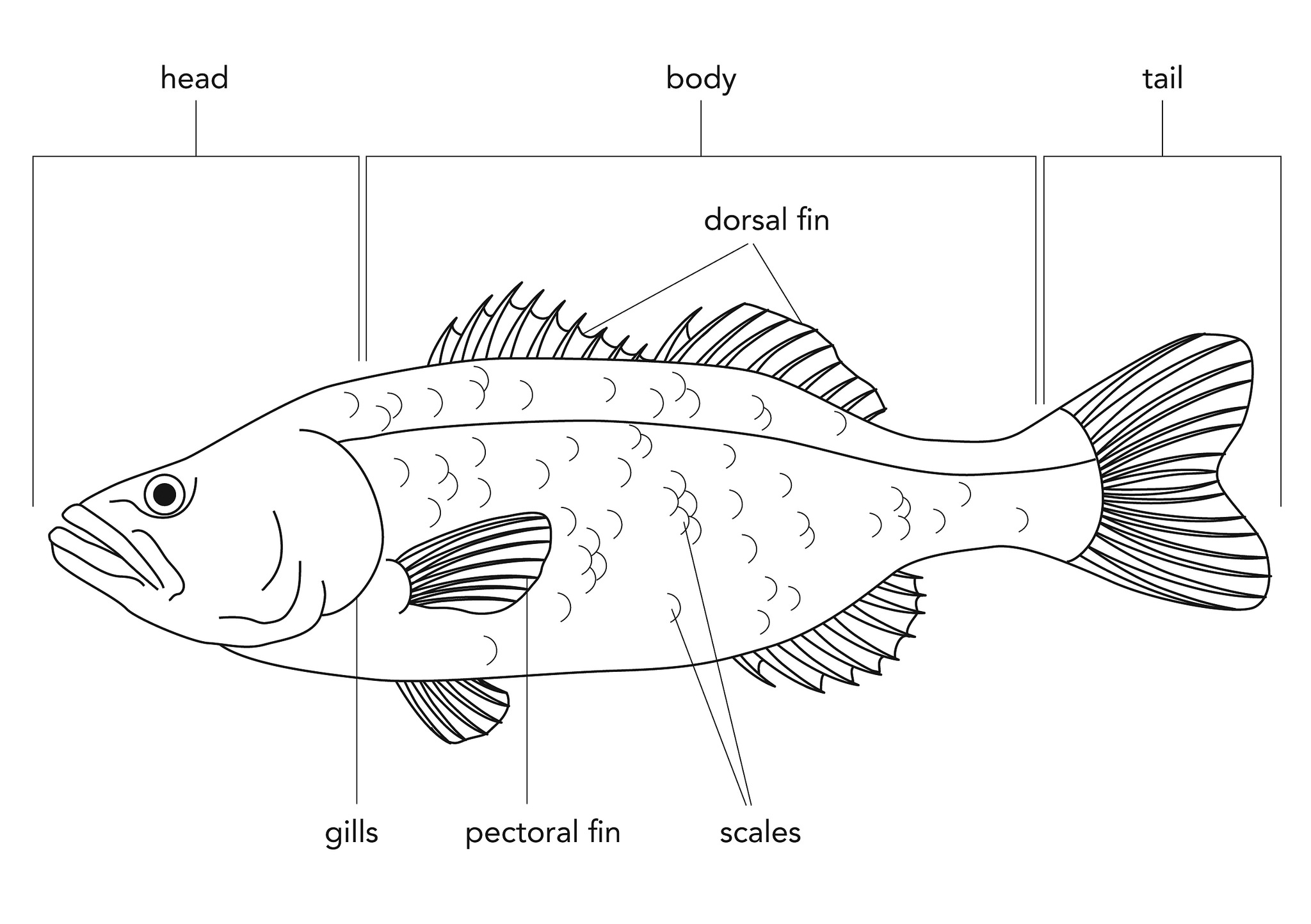
3. Have a look at this image with the parts of a fish. Learn them. Then make a list with the most common fish in your area. Search photographs on the Internet and see if you can identify their different parts. |
||
4. BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE is a system used by scientists to name plants and animals by means of two names. The first one corresponds to the genus and the second to the species. The first one is written in capital letters and the second in small letters. The entire two-part name must be written in italics. Examples may be Quercus robur, which is an oak tree or Homo sapiens, which represents human beings. Find at least ten species which are in danger of extinction in our country and write their binomial nomenclature. |
||
Dian Fossey
Projects
|
PROJECT 1 Search the school, or your garden, etc. to find invertebrates. Take a photo of them and make a fact sheet for each of them. Then create a slideshow with the photos so that you can show the rest of the class.
PROJECT 2 Are there any species in danger of extinction in your country / area? Make a poster with all of them. What actions are being held to protect them? |
PROJECT 3 |
|
|
Watch this video about the dissection of a trout to see its internals parts. Then do the same at the laboratory with a typical fish from your area. Dissection of a trout. Patrick Cross. YouTube. (YouTube Standard Licence) |
||
Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike License 4.0


.jpg)